QR codes in Trezor Suite
A QR code, or Quick Response code, is a two-dimensional machine-readable barcode that can be used to represent an address. The use of a QR code makes it easy to scan an address, rather than having to type or copy it.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Using QR code addresses in Trezor Suite
- Why use a QR code?
- How does a QR code work?
Using QR code addresses in Trezor Suite
Trezor Suite shows receiving wallet addresses as QR codes, so they can be easily scanned from a mobile device or using another camera:
- In the account Receive tab, click on Show full address:

- Trezor Suite will display the full BTC receiving address as both an alphanumeric string and as a QR code
- After carefully checking the address in Trezor Suite and on your Trezor device, you must confirm the BTC receiving address using your Trezor device:

- As well as displaying the QR code in Trezor Suite, after clicking the Show full address button (or 'Reveal address' in the list of addresses already generated for a specific account) you can also press the 'QR' button on your Trezor to display the QR code on the device itself:

- You can toggle between 'Address' and 'QR' format using the corresponding button on the Trezor device.
- Tip: once the address is confirmed using your Trezor device, you can then use the 'Copy address' button in Trezor Suite to eliminate errors when specifying the receiving address:

If given access to a camera, Trezor Suite can also scan QR codes of an address to send funds to:
- In the account Send tab, just above the Address input field you can find the QR 'Scan' button:
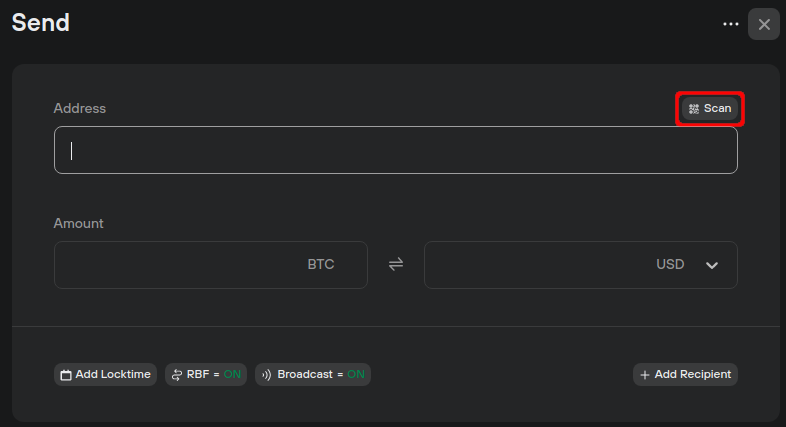
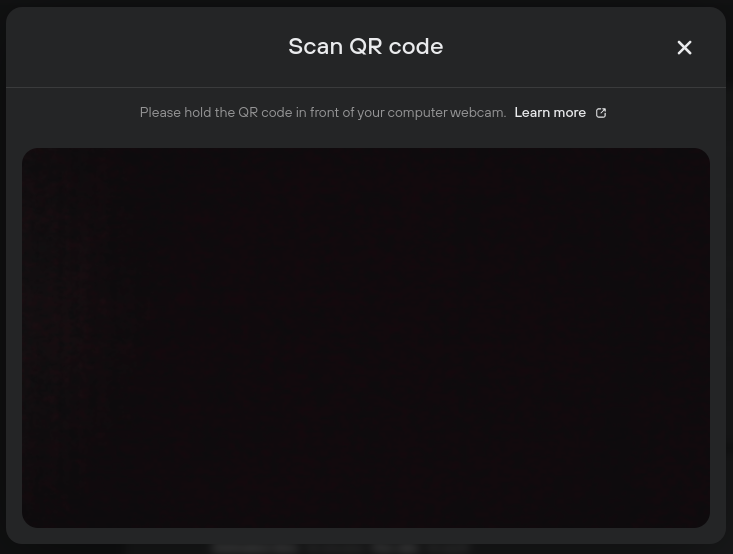
- After allowing permission for Trezor Suite to access your camera, present the necessary QR code to the camera, which contains the desired address information (and possibly other transaction information):
Why use a QR code?
When using Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies to pay at the point-of-sale or for a face-to-face transaction, there is the problem of how to communicate the receiving address in a way that the person paying can use. A Bitcoin address is between 27 and 34 characters long. This takes time to type manually, and it is easy to make a mistake.
On the other hand, a QR code can quickly and reliably represent this amount of data in a machine-readable manner. The QR code can (potentially) contain other information as well, such as an amount and a message.
With a mobile phone, a convenient way to pass that data is for the payment recipient (e.g., a merchant) to display a QR code with the Bitcoin address for the transaction, and then for the person paying to scan that code to obtain the address.
It is also possible to print out the QR code containing the user's receiving address and hand it to the sender, who can use it for repeated or regular payments.
How does a QR code work?
As mentioned above, a QR code is a two-dimensional barcode that contains machine-readable information in a convenient manner. It was first designed in 1994 for the automotive industry in Japan and has since expanded to a wide range of applications. Where a traditional barcode presents a string of information as a one-dimensional line of black and white bars, a two-dimensional barcode packs significantly more information into a grid of black and white squares. It contains the following information:
- Quiet zone: The empty white border is making it possible to identify the code among other printed information.
- Finder patterns: Larger black and white squares in three of the corners. They differentiate QR codes from other types of barcodes and make the orientation of the code clear.
- Alignment pattern: Ensures the code can be deciphered even if the code is distorted.
- Timing pattern: Makes it easy to identify the individual data cells within a QR code and is especially useful when the code is damaged or distorted.
- Version information: Identifies the specific standard of the QR code.
- Data cells: Contain some of the actual data in the code.